Nile Crocodile Habitat Mapping Efforts by Researchers
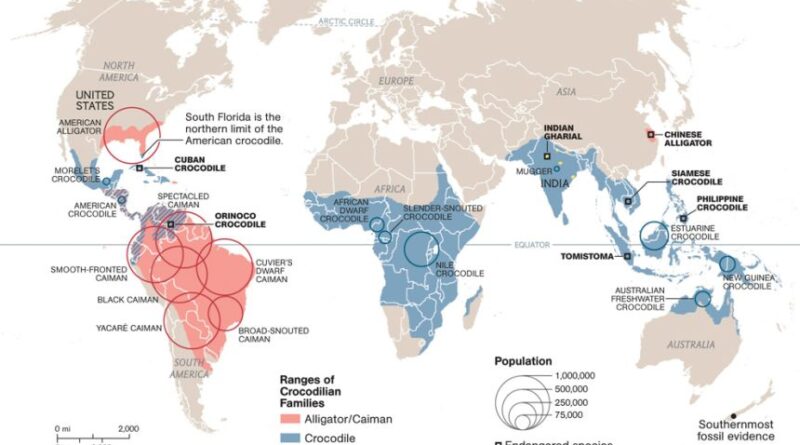
Nile Crocodile Habitat Mapping Efforts by Researchers The Nile crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus) is one of the largest and most formidable reptiles, found across Africa’s freshwater systems. As an apex predator, it plays a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. However, increasing human activities, habitat degradation, and climate change pose significant threats to their survival. To address these challenges, researchers have undertaken extensive habitat mapping efforts to better understand and protect this iconic species.
The Importance of Habitat Mapping

Mapping the habitats of Nile crocodiles is crucial for identifying areas critical for their breeding, nesting, and foraging. Such information aids in conservation planning, mitigates human-wildlife conflicts, and ensures sustainable coexistence between crocodiles and local communities. Habitat mapping also helps assess the impact of environmental changes, such as deforestation and water management projects, on crocodile populations.
Table: Summary of Nile Crocodile Habitat Mapping Efforts
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Species | Nile crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus) |
| Distribution | Africa’s freshwater systems, including rivers, lakes, wetlands, and estuaries |
| Objectives | – Identify critical habitats (breeding, nesting, foraging) – Assess habitat degradation and threats – Support conservation planning and policy-making |
| Research Methods | – Data Collection: Satellite imagery, remote sensing, ground surveys – Technology: GPS tracking, drones, GIS |
| Collaborators | Local communities, conservation organizations, ecologists, geographers, and data scientists |
| Key Findings | – Identified habitat hotspots and migratory corridors – Seasonal movement patterns – Impacts of deforestation and infrastructure projects |
| Challenges | – Accessibility to remote habitats – Limited funding – Human-wildlife conflicts |
| Applications | – Designation of protected areas and buffer zones – Informing environmental impact assessments – Community engagement and education |
| Future Directions | – Expanding research to under-studied regions – Incorporating climate change models – Strengthening cross-border conservation |
| Significance | – Ensures long-term survival of Nile crocodiles – Protects biodiversity and ecosystems – Balances human and wildlife coexistence |
Objectives of the Research

The primary goals of these mapping efforts are to pinpoint crucial habitats, evaluate the extent of habitat degradation, and prioritize areas for conservation. This work also seeks to provide data for policy-making and foster better management of human activities that threaten these crocodile habitats.
Research Methods
To achieve these objectives, researchers have employed a combination of advanced technologies and fieldwork techniques:
- Data Collection: Satellite imagery and remote sensing are used to analyze large landscapes, while ground surveys help locate nesting sites and monitor crocodile movements.
- Technology Integration: GPS tracking devices attached to individual crocodiles allow researchers to study their movement patterns in detail. Drones provide aerial views of habitats, revealing areas that are otherwise inaccessible. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are used to compile and analyze this data to create detailed habitat maps.
- Collaborative Efforts: Local communities and conservation organizations play an essential role in gathering data and addressing conservation challenges. Collaboration among ecologists, geographers, and data scientists ensures a multidisciplinary approach.
Key Findings

Mapping efforts have yielded significant insights into the habitat preferences and behavior of Nile crocodiles. Researchers have identified critical hotspots for breeding and feeding, as well as migratory corridors that connect different populations. The studies have also revealed the detrimental effects of environmental changes, such as the loss of nesting areas due to dam construction and water pollution. Seasonal movement patterns were documented, highlighting the crocodiles’ reliance on specific habitats during breeding and drought periods.
Challenges in Habitat Mapping
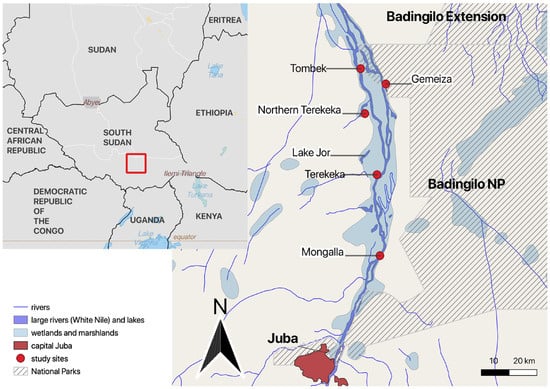
Despite these advancements, researchers face several challenges. Accessing remote and sometimes dangerous habitats can be difficult and time-consuming. Limited funding often hampers the use of advanced technology and restricts the scope of field studies. Additionally, conflicts with local human activities, such as agriculture and fishing, further complicate conservation efforts.
Applications of the Research
The findings from habitat mapping have practical applications in conservation and policy-making. Identified hotspots can be designated as protected areas or buffer zones to safeguard the crocodiles and their ecosystems. Public awareness campaigns and local community engagement are strengthened by scientific data, fostering support for conservation initiatives. The research also informs environmental impact assessments for development projects, ensuring they are designed with minimal harm to crocodile habitats.
Future Directions
Looking ahead, researchers aim to expand their studies to under-explored regions, integrating climate change models into habitat mapping to predict future challenges. Cross-border conservation efforts will also be crucial, as many Nile crocodile habitats span national boundaries. Strengthening international cooperation will help ensure the long-term survival of these reptiles.
Conclusion
Habitat mapping is a critical tool for understanding and protecting the Nile crocodile. By combining technological innovations with collaborative research, scientists are making significant strides in conserving this species. However, continued efforts, funding, and international collaboration are essential to mitigate the threats facing these apex predators. Protecting the Nile crocodile means preserving the health of Africa’s freshwater ecosystems, which benefits biodiversity and human communities alike.
Tips for Effective Nile Crocodile Habitat Mapping
Leverage Advanced Technology
- Use high-resolution satellite imagery and drones to identify remote and hard-to-reach habitats.
- Equip Nile crocodiles with GPS trackers to monitor their movement and behavior in real-time.
Integrate Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
- Combine spatial data with environmental variables (e.g., water quality, vegetation) to create detailed and actionable habitat maps.
- Use GIS to model habitat suitability and predict impacts of environmental changes.
Involve Local Communities
- Engage local populations to gather traditional ecological knowledge about crocodile habitats and behaviors.
- Provide training to local communities for monitoring and reporting habitat changes.
Conduct Field Surveys Strategically
- Schedule surveys during critical periods like breeding or nesting seasons to collect focused and relevant data.
- Use safety protocols to ensure the well-being of researchers in crocodile-dense areas.
Collaborate Across Disciplines
- Partner with ecologists, hydrologists, and conservation organizations to share resources and expertise.
- Foster international collaboration, especially for habitats spanning multiple countries.
Address Threats Holistically
- Monitor human activities near crocodile habitats, such as agriculture, fishing, and tourism, to understand their impacts.
- Advocate for policies to mitigate habitat degradation caused by infrastructure projects, such as dams or urbanization.
Utilize Public Awareness Campaigns
- Share findings through accessible materials like maps and infographics to inform and educate stakeholders.
- Promote coexistence strategies to reduce human-wildlife conflicts in shared habitats.
Secure Adequate Funding
- Seek grants from conservation organizations and international funding bodies.
- Highlight the ecological and cultural importance of Nile crocodiles to attract support.
Plan for Long-Term Monitoring
- Establish periodic surveys to track changes in habitat use over time.
- Build a database for consistent data collection and analysis across years.
Incorporate Climate Change Projections
- Study how changing rainfall patterns, water levels, and temperatures could alter crocodile habitats.
- Adapt conservation strategies to account for predicted future scenarios.
By following these tips, researchers and conservationists can enhance the effectiveness of habitat mapping efforts, ultimately contributing to the long-term survival of the Nile crocodile and its ecosystems.
FAQs: Nile Crocodile Habitat Mapping Efforts
Why is habitat mapping important for Nile crocodiles?
Habitat mapping helps identify critical areas for breeding, nesting, and foraging, enabling conservationists to protect these zones. It also informs strategies to reduce human-wildlife conflicts and supports sustainable ecosystem management.
What methods are used in habitat mapping?
Researchers use advanced technologies like GPS trackers, drones, satellite imagery, and Geographic Information Systems (GIS). Ground surveys and collaboration with local communities are also key components.
What challenges do researchers face in mapping habitats?
Challenges include:
- Difficulty accessing remote or dangerous areas
- Limited funding and resources
- Conflicts between human activities (farming, fishing) and crocodile conservation
How do researchers track Nile crocodiles?
GPS tracking devices are attached to individual crocodiles to monitor their movement and behavior. This data is then analyzed to understand habitat use and seasonal migration patterns.
What are the main threats to Nile crocodile habitats?
The main threats include:
- Habitat destruction due to deforestation and dam construction
- Water pollution and declining water quality
- Human encroachment and land-use changes
How does this research benefit local communities?
By identifying areas of potential conflict, researchers help design solutions that protect both human livelihoods and crocodile populations. Public awareness campaigns also educate communities on the ecological importance of crocodiles.
Are there international efforts to protect Nile crocodile habitats?
Yes, many habitats span across borders, requiring international cooperation. Cross-border conservation programs and agreements help protect migratory corridors and shared ecosystems.
How do researchers address climate change impacts on habitats?
Researchers incorporate climate models to predict future changes in rainfall, water levels, and temperature. This helps design adaptive conservation strategies to mitigate climate impacts.
What are the future goals of habitat mapping?
Future goals include expanding research to under-studied regions, integrating climate change data, and strengthening partnerships between nations for transboundary conservation efforts.
How can the public contribute to Nile crocodile conservation?
The public can support conservation efforts by:
- Advocating for policies that protect crocodile habitats
- Participating in awareness campaigns and community programs
- Supporting organizations involved in habitat mapping and wildlife conservation